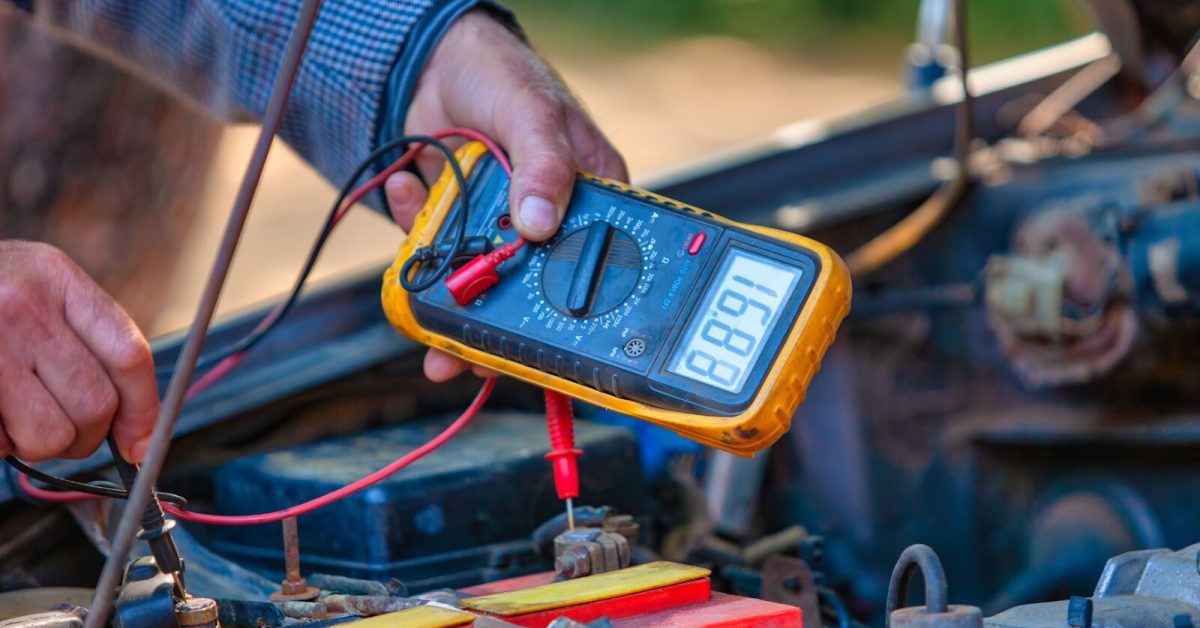
Technician using a multimeter to test which vehicle instrument measures the voltage in a vehicle’s electrical system.
Modern vehicles are full of complex electrical components, from dashboard lights to advanced safety systems. Knowing how to measure voltage in these systems isn’t just helpful’s essential. The right tools and understanding can keep your car running smoothly and help avoid costly repairs down the line. A simple voltage reading can reveal whether your battery is strong or struggling to keep up. Understanding what your vehicle’s voltage meter tells you is one of the easiest ways to stay ahead of potential electrical failures.
What Is the Role of a Voltage Meter in a Vehicle?

A voltage meter, commonly referred to as a voltmeter, is the primary instrument that measures the voltage in a vehicle’s electrical system. It determines the potential difference between two points in an electrical circuit, which in automotive contexts typically involves assessing the health and output of the battery and alternator. This device plays a crucial role in identifying whether the battery voltage is within the optimal range, ensuring the proper function of various electronic devices embedded within the vehicle.
When the vehicle is off, a healthy battery should read around 12.6 volts. When the engine is running, the voltage should rise to between 13.7 and 14.7 volts due to the alternator charging the battery (U.S. Department of Energy). By using a voltage meter, auto repair technicians can quickly diagnose electrical issues that may not be immediately visible, such as faults in the alternator, failing batteries, or poor connections within the wiring.
How Does a Voltage Meter Help Diagnose Electrical Issues?

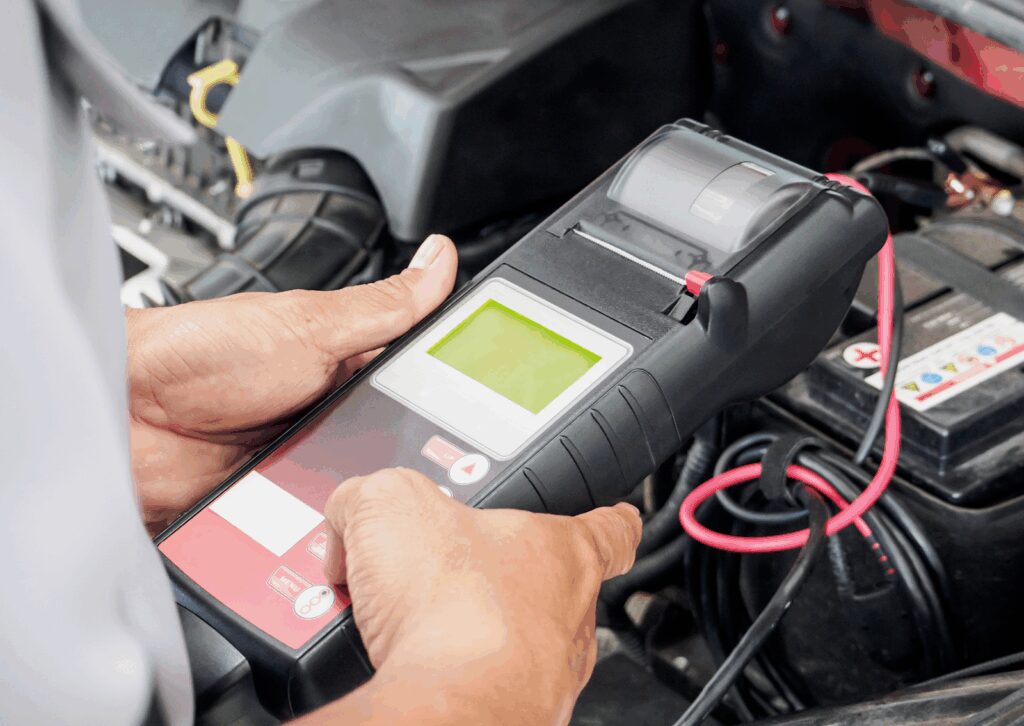
The ability to measure voltage accurately allows technicians to troubleshoot problems that could lead to serious mechanical failures if left unresolved. For instance, an underperforming battery might cause intermittent starting issues or erratic performance of lights and infotainment systems. A voltage meter helps identify these faults before they escalate.
To diagnose electrical issues, the technician connects the red probe of the voltmeter to the positive terminal of the battery and the black probe to the negative. This two-point measurement provides insights into whether the battery is delivering the correct voltage. In some cases, a voltage drop test across various electrical components or wiring segments may reveal resistance problems that impede the flow of electricity, which a voltage meter can highlight effectively.
Why Are Electrical Components So Dependent on Accurate Voltage Readings?

Every modern vehicle includes a host of electrical components, from fuel injectors to HVAC systems to electronic control units. These systems rely on a consistent, regulated voltage to operate correctly. Even slight deviations in battery voltage can cause malfunctions in these electronics, especially in sensitive devices like engine sensors or control modules.
Accurate measurements ensure that each component is receiving the appropriate voltage. Without these readings, the functionality of components such as lighting, ignition, infotainment, and safety systems can be compromised. In short, maintaining the electrical system’s balance is essential to overall vehicle performance.
What Is a Multimeter and How Is It Used in Automotive Diagnostics?
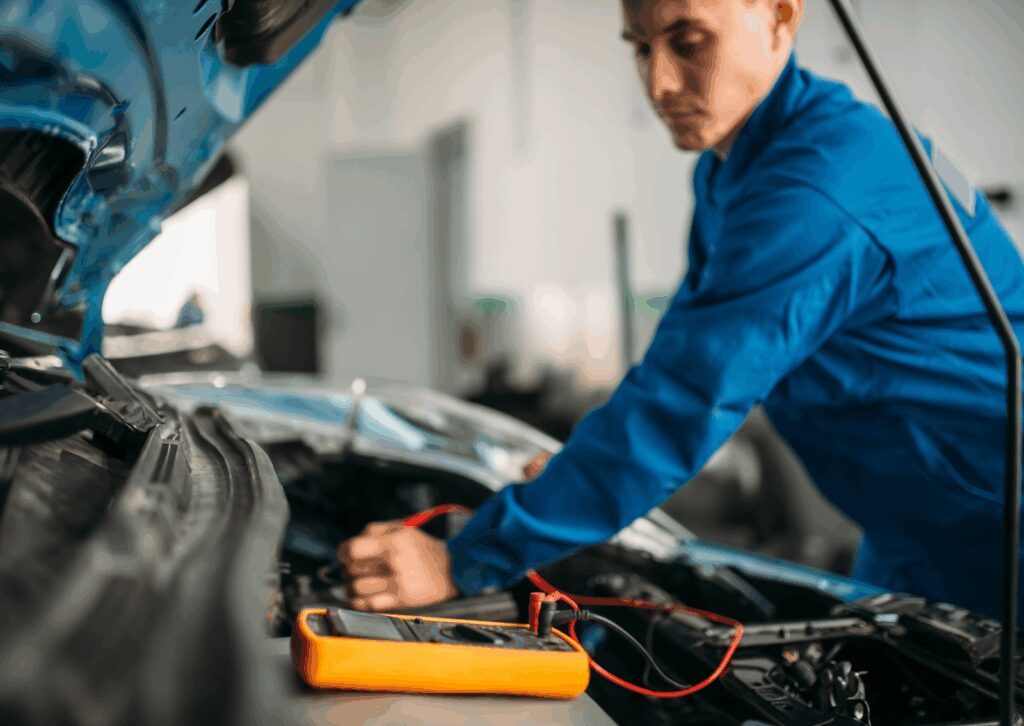

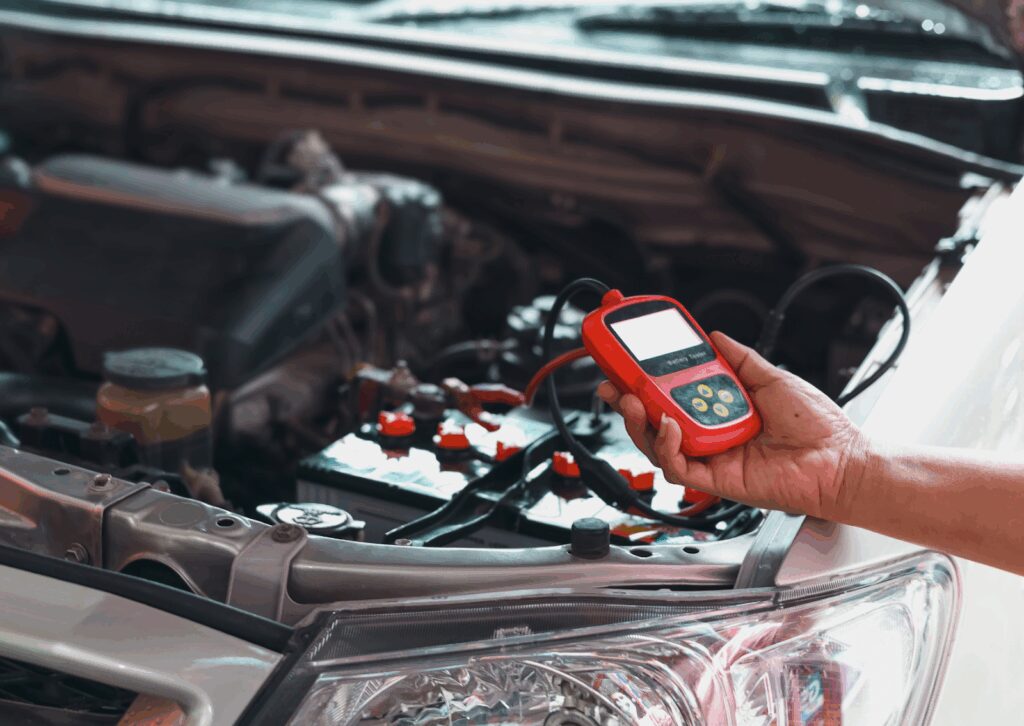
A multimeter is a versatile tool that combines the functions of a voltmeter, ammeter, and ohmmeter into one device. Automotive technicians use digital multimeters to test for voltage, current, and resistance within a vehicle’s electrical systems. These tools are essential in automotive diagnostics because they provide more comprehensive information than a standalone voltmeter.
To test a battery, for example, a technician would set the multimeter to DC voltage, connect the test leads appropriately (red probe to positive, black probe to negative), and read the output on the digital screen. This helps determine whether the battery is undercharged, overcharged, or functioning correctly. The multimeter can also be used to test continuity, allowing technicians to troubleshoot faults in wiring or connections.
How Do Electrical Systems in Vehicles Differ from Industrial Settings?

While the core principles of electricity apply universally, electrical systems in vehicles are often more compact and subjected to different environmental stresses compared to those in industrial settings. Automotive electrical systems must be designed to withstand vibrations, temperature fluctuations, and moisture.
In industrial maintenance, voltmeters and multimeters are also used to test larger-scale electronics such as solar panels, HVAC systems, and complex control circuits. These systems typically operate on higher voltage and current levels, requiring additional safety precautions. However, the process to measure voltage and troubleshoot electrical issues is fundamentally similar across both settings.
What Safety Precautions Should Be Taken When Testing Electrical Circuits?

Testing vehicle electrical systems involves inherent risks, particularly when dealing with live circuits. Safety precautions are essential to protect both the technician and the vehicle. Before testing, it is important to turn off the ignition and disconnect the battery if checking resistance to avoid damaging the multimeter or components.
Always inspect the test leads for damage, use the correct measurement settings, and ensure the probes do not touch each other during testing. When connecting the red probe and black probe to measure voltage, make sure the connections are secure. Using insulated tools and wearing safety goggles are also recommended practices. These steps reduce the likelihood of shorts, shocks, or unintended arcing.
How Do You Accurately Measure Voltage in a Vehicle?

To measure voltage accurately, set the multimeter to the correct voltage range (typically DC voltage for automotive systems). Connect the red probe to the positive terminal or wire and the black probe to the ground or negative terminal. The digital screen will display the measured voltage.
If measuring voltage at a switch, outlet, or other component, identify the two points in the circuit to test. This may involve back-probing connectors or accessing fuse boxes. Consistent voltage readings indicate proper circuit function, while unexpected drops could signal problems such as corroded connections or damaged wires.
Accurate measurements are essential in determining whether systems like lighting, ignition, and fuel delivery are working as intended. Without them, technicians would be left guessing about the root causes of issues.
How Can Routine Electrical Testing Prevent Costly Repairs?

Routine testing of a vehicle’s electrical components using a voltmeter or multimeter can help identify potential issues early. For example, catching a weak battery before it fails completely can prevent inconvenient breakdowns. Similarly, identifying shorts or excessive resistance in wiring can stop overheating and prevent fires.
Regular inspections of the car’s electronics can also detect degraded switches, failing relays, and issues in the ventilation or heating circuits. By measuring voltage and resistance in these systems, auto repair technicians can ensure that the vehicle operates safely and efficiently.
Preventive diagnostics play a critical role in extending a vehicle’s life. According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), electrical system failures are among the top causes of vehicle malfunctions (NHTSA.gov). Through consistent testing, you reduce risks and avoid higher repair costs.
What Are the Best Practices for Using a Voltage Meter in Auto Shops?

Professional auto shops follow a systematic process when using a voltage meter. First, they identify the circuit or component to be tested, then disconnect any power if testing for resistance. When measuring voltage, they follow safety protocols and ensure that the test leads are firmly connected.
Technicians understand the behavior of electricity within different systems, such as how capacitors hold a charge or how a switch regulates the flow. They look for abnormal voltage drops, examine the continuity of wiring, and test the functionality of outlets and devices under real operating conditions.
Additionally, professional diagnostic tools often include digital enhancements like graphing voltage over time, which provides more detailed insights into intermittent faults. These practices contribute to efficient troubleshooting and reduce the time required for repairs.
Why Should You Trust Local Experts for Electrical Auto Repair?

When it comes to diagnosing and repairing electrical issues in vehicles, local professionals offer both expertise and convenience. AtMetric Motors, their ASE-certified technicians use advanced tools to perform electronics testing and accurately measure voltage throughout your vehicle’s systems.
Their services cover everything from routine diagnostics to complex troubleshooting involving HVAC systems, battery voltage assessments, and lighting repairs. With a deep understanding of how electrical circuits and components function, they ensure your vehicle receives top-tier care.
Don’t wait for a warning light to become a breakdown. Trust the experts at Metric Motors to help you maintain your vehicle’s essential electronics with accuracy and professionalism. Schedule a service or learn more.
What Is the Final Takeaway on Measuring Vehicle Voltage?
Understanding which instrument measures the voltage in a vehicle’s electrical system can help both drivers and technicians address problems proactively. A voltage meter or multimeter is essential for diagnosing faults, ensuring functionality, and keeping systems operating within their designed parameters.
Whether you’re maintaining your vehicle at home or relying on a certified technician, accurate testing and regular inspections are vital. With complex electronics becoming more common in modern cars, staying ahead of potential issues ensures safety, efficiency, and peace of mind on the road.
Works Cited
National Highway Traffic Safety Administration. “Vehicle Electrical System Safety.” NHTSA.gov, www.nhtsa.gov/technology-innovation/vehicle-electrical-system-safety. Accessed 18 June 2025.
U.S. Department of Energy. “Maintaining and Testing Car Batteries.” Energy.gov, www.energy.gov/energysaver/maintaining-and-testing-car-batteries. Accessed 18 June 2025.
Society of Automotive Engineers. “Automotive Electrical Diagnostics Best Practices.” SAE International, www.sae.org. Accessed 18 June 2025.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the purpose of a voltage meter in my car?
A voltage meter, or voltmeter, measures the voltage in your vehicle’s electrical system. It helps monitor battery health and detect issues in components like the alternator, wiring, or sensors before they cause major problems.
2. How do I know if my vehicle's electrical system is working properly?
You can check by using a multimeter to test the battery voltage. A healthy battery should read around 12.6 volts when the engine is off and 13.7 to 14.7 volts when running. Any major deviation may indicate an underlying issue.
3. What’s the difference between a voltmeter and a multimeter?
A voltmeter strictly measures voltage, while a multimeter can also measure current and resistance. Multimeters are more versatile and commonly used in auto diagnostics to troubleshoot various electrical issues.
4. Can electrical problems really lead to expensive repairs?
Yes. Ignoring small electrical faults—like low battery voltage, poor wiring connections, or malfunctioning components—can lead to breakdowns or damage to more expensive systems like the ECU or HVAC controls.
5. Should I test my car’s electrical system regularly?
Absolutely. Routine voltage checks can reveal battery weakness, faulty alternators, or deteriorating circuits early. Regular diagnostics help maintain your vehicle’s functionality and safety, saving you money in the long run.